Radiotherapy treatment of different types of cancer
New Technology in Radiotherapy
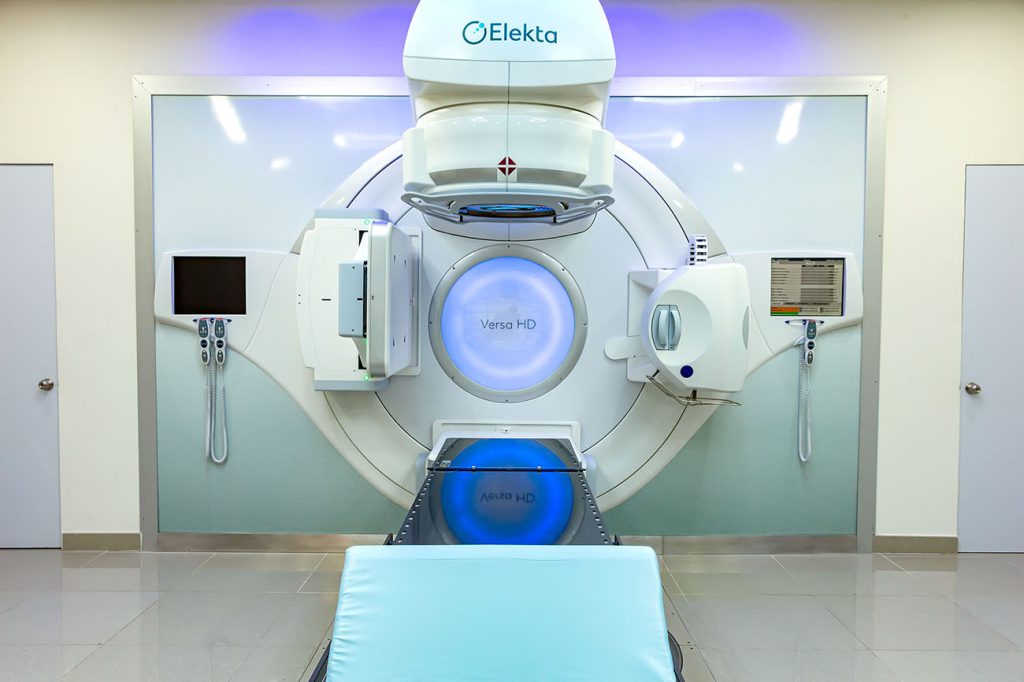
Our ELEKTA Versa HD radiotherapy equipment; It has the most advanced configuration at the national level, which integrates the most sophisticated components on the market, which translates into greater precision, safety and effectiveness.
We provide highly specialized treatments, from conventional treatments with standard techniques, to the most modern and cutting-edge treatments with the most advanced techniques.
Conventional Radiotherapy Techniques
What are they and how are they used?
Superficial Radiotherapy (with Electrons)
This technique contemplates electron-based radiotherapy which ensures maximum dose delivery to the patient's skin. It is used mostly for cases of skin cancer, as well as to improve aesthetics in keloid healing
Radiotherapy in 2 Dimensions (2D)
2D radiotherapy allows only simple treatments and is generally used for palliative treatment. This technique contemplates doses with protections for treatments with Photon and Electron energies with simple fields.
Radiotherapy in 3 dimensions (3D)
This technique contemplates homogeneous doses to the target volume of treatment. It uses a 3D simulation Tomography (CT) for its calculation, and protections for treatments with Photons and Electrons. Usually 1 to 6 fields are used. Compared with 2D radiation therapy, 3D conformal radiation therapy delivers radiation to cancer cells more precisely while reducing the amount of radiation to healthy tissue. This conventional form of radiation therapy is used to treat cancerous and noncancerous tumors throughout the body.
Advanced and Precise Radiotherapy Techniques
Dynamic radiation therapy in modulated Intensity (IMRT):
This technique contemplates multiple treatment fields to concentrate doses in the tumor, allowing modulating the intensity in the area to be treated. Generally more than 6 treatment fields are used. IMRT often requires multiple (split) treatment sessions on different days. The Radio Oncologist doctor takes into account the type, location and size of the tumor, the doses to normal structures, and the health of the patient to decide the number of treatments. At the beginning of the treatment session, the radiation therapist places the patient on the table, and is guided by the markings on the skin (tattoo) that define the treatment area. If they use immobilization systems which will be used to keep the patient in the proper position. The patient may need to be placed in another position during the procedure.
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (V-MAT)
This technique achieves greater precision than IMRT in less time, which could allow higher doses to the tumor and greater protection to healthy organs. The VMAT delivers a continuous beam of radiation therapy in one or more arcs that move around the treatment area. Automatically changes beam shape and radiation dose as you move. VMAT treatment sessions are generally shorter than IMRT, around 10 minutes.
Adaptive Radiotherapy in 4 dimensions (4D)
This technique contemplates homogeneous doses to the target volume of treatment. It uses CBCT (Cone-beam computed tomography) images in real time that allows adjusting the volume of the treatment to the maximum. It not only acquires the images at a specific moment, but also a series of images are acquired with the treatment area in the different positions that it can adopt. In 4D Radiotherapy these images can be represented by reproducing the actual movement of the patient. For example, in breast cancer, thanks to these technical resources, toxicity in adjacent organs can be reduced by at least 5% and to a large extent also the side effects caused by cancer treatments. This means that there is much more safety and health, since organs such as the heart are much less affected.
Cranial Stereotaxic Radiosurgery
They are outpatient procedures which are used as an alternative to surgical procedures. Cranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Fractionated Cranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRT) techniques avoid cerebral incisions, decreasing morbidity and/or sequelae, with a similar or even higher probability of success, at a lower cost and lower risk in comparison to a surgical procedure in the operating room. This procedure is ambulatory and non-invasive. There are two types of cranial stereotaxic radiosurgery:
• Cranial Stereotaxic Radiosurgery (SRS): This technique delivers a very high dose of radiotherapy in a single fraction. It is a modern and precise therapeutic technique in which small volumes of the skull are irradiated with high doses of radiation. A precise immobilization and fixation technique is needed, specific software, medical experience, and the possibility of using and fusing Tomography (CT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (NMR), Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and digital angiography images. This makes it possible to locate a specific point in the brain. This procedure is ambulatory and non-invasive.
• Fractionated Cranial Stereotaxic Radiosurgery (SRT): This technique delivers a very high dose of intracranial radiotherapy ofone to five fractions. It is a very useful tool for the treatment of malignant cranial lesions in pediatric patients, since it reduces the amount of radiation that the patient receives and, in this way, prevents toxicity from significantly affecting the cognitive functions of patients. . It is especially beneficial for head and neck tumors. This procedure is ambulatory and non-invasive
Stereotaxic Ablative Body Radiosurgery (SABRT)
This technique provides a very high dose of extracranial radiotherapy of one and up to 5 fractions. The procedure uses multiple, precisely focused radiation entry sites to treat tumors and other problems throughout the body. Stereotaxic body radiation therapy is used to treat tumors in the lungs, spine, liver, neck, lymph nodes, or other soft tissue, thereby avoiding surgical procedures.
Hypofractionated Treatments
It is an external radiotherapy technique that could reduce in selected medical cases the number of radiotherapy sessions that the patient receives with the same effectiveness as a conventional treatment, making it more convenient for the patient to attend fewer days while maintaining the standards of effectiveness and safety in the process.
Examples:
– Prostate Cancer with conventional fractionation which is treated in 43 business days, could be
reduced to 20 business days.
– Breast Cancer with conventional fractionation which is treated in 25 business days, could be
reduced to 15 business days
Benefits:
- We have a versatile team that allows us to treat practically any type and location of malignant tumors and benign pathologies , offering highly specialized treatments with innovative world-class technology.
- Greater speed, comfort and safety: reliable, fast and safe technology that helps to considerably reduce treatment time compared to other equipment.
- Submillimeter precision: the Four-Dimensional (4D) Imaging System allows adapting to the shape and size in real time by scanning the tumor or tumor bed and even following the patient’s breathing during treatment thanks to the «Active Breathing Coordinator» (ABC) application. ), in addition to having a Robotic Fixation System (HexaPOD™) that allows the treatment table to be rotated to
adjust the position of the patient, irradiating with greater precision and safety.
- Our team offers a wide variety of possibilities for radiotherapy treatments with
techniques such as: Superficial Radiotherapy, 2D, 3D, 4D, Dynamic IMRT, V-MAT,
and Cranial and Body Radiosurgery (SRS, SRT, and SABRT).
- Treatment of benign tumors (arteriovenous malformations, pituitary
macroadenoma, meningiomas, trigeminal neuralgia, acoustic neurinoma or
vestibular schwannoma).
- Treatments to improve the aesthetics of keloid scarring.

